23. “Conjugated Oligomers with Stable Radical Substituents: Synthesis, Single Crystal Structure, Electronic Structure, and Excited State Dynamics”. Huang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Jin, S.; Li, C.; Warncke, K.; Evangelista, FA.; Lian, T.; Egap, E. Chemistry of Materials. 2018, 30, 7840-7851. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.8b03366
22. “Open shell organic semiconductors: an emerging class of novel materials with novel properties”. Huang, Y; Egap, E. Polymer Journal. 2018, 50, 603-614. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41428-018-0070-6
21. “Semiconductor Quantum Dots as Photocatalysts for Controlled Light-Mediated Polymerizations” Huang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Egap, E. ACS Macro Lett. 2018, 7, 184-189. Highlighted by Rice News, ScienceDaily.com, phys.org, SciTechDaily, AAAS EurekAlert, others
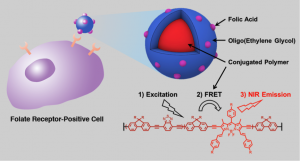
20. “Triblock Near-Infrared Fluorescent Polymer Semiconductor Nanoparticles for Targeted Imaging,” Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, D.; Pollard, A. C.; Chen, Z.; Egap, E. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 5685-5692. Invited Article, Special issue of Emerging Young Investigators
19. “Alignment and Charge Transport of One-Dimensional Conjugated Polymer Nanowires in Insulating Polymer Blends,” Chang, M.; Su, Z.; Egap, E. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 9449-9456. DOI:10.1021/acs.macromol.6b01721.
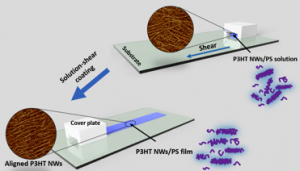
18. “Macroscopic Alignment of One-Dimensional Conjugated Polymer Nanocrystallites for High Mobility Organic Field Effect Transistors,” Chang, M.; Choi, D.; Egap, E. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 13484-13491.

17. “Colorimetric Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogel Polymers for the Detection of Nerve Agent Surrogates,” Beleger, C.; Weis, J. G.; Egap, E.; Swager, T. M. Macromolecules, 2015, 48, 7990-7994.
16. “Fluorescent Multiblock π-Conjugated Polymer Nanoparticles for in Vivo Tumor Targeting,” Ahmed, E.; Morton, S. W.; Hammond, P. T.; Swager, T. M. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 4504-4510.
15. “Photoinduced Hole Transfer is Suppressed with Diminished Driving Force in Polymer-Fullerene Solar Cells, While Electron Transfer Remains Active,” Ren, G.; Schlenker, C. W.; Ahmed, E.; Subramaniyan, S.; Olthof, S.; Kahn, A.; Ginger, D. S.; Jenekhe, S. A. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 1238-1249.
14. “Nanowires of Oligothiophene-Functionalized Naphthalene Diimide: Self-Assembly, Morphology, and All-Nanowire Bulk Heterojunction Solar Cells,” Ren, G.; Ahmed, E.; Jenekhe, S. A. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 24373-24379.
13. “Non-Fullerene Acceptor-Based Bulk Heterojunction Polymer Solar Cells: Engineering the Nanomorphology via Processing Additives,” Ren, G.; Ahmed, E.; Jenekhe, S. A. Adv. Energy Mater. 2011, 1, 946-953.
12. “Oligothiophene-Functionalized Naphthalene Diimides: Synthesis, Self-Assembly of Nanowires, Electron Transport, and Use as Acceptor in Solar Cells,” Ahmed, E.; Ren, G.; Kim, F. S.; Hollenbeck, E. C.; Jenekhe, S .A. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 4563-4577.
11. “Benzobisthiazole-Based Donor Acceptor Copolymers for Organic Field-Effect Transistors and Photovoltaic Cells,” Ahmed, E.; Subramaniyan, S.; Kim, F. S.; Xin, H.; Jenekhe, S. A. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 7207-7219.
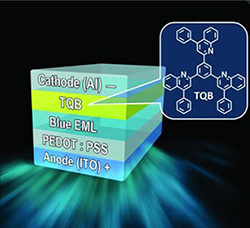
10. “Solution-Processable Electron Transport Materials for Highly Efficient Blue Phosphorescent OLEDs,” Ahmed, E.; Earmme, T.; Jenekhe, S. A. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 3889-3899.
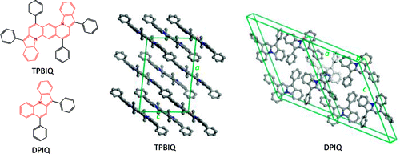
9. “Charge Transport of the Tetraphenylbis(indolo[1,2-a])quinoline and 5,7-Diphenylindolo[1,2-a]quinoline Crystals,” Zhu, L.; Kim, E.-G.; Yi, Y.; Ahmed, E.; Jenekhe, S. A.; Coropceanu, V.; Brédas, J.-L. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 20401-20409.
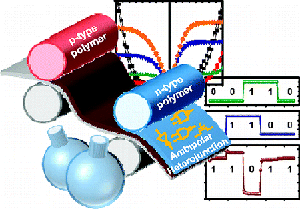
8. “Air-Stable Ambipolar Field-Effect Transistors and Complementary Logic Circuits from Solution-Processed n/p Polymer Heterojunctions,” Kim, F. S.; Ahmed, E.; Subramaniyan, S.; Jenekhe, S. A. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2010, 2, 2974-2977.
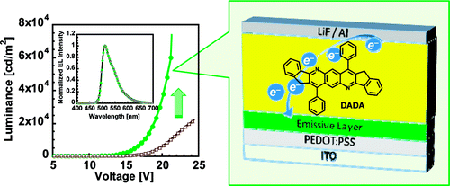
7. “Solution-Processed Highly Efficient Blue Phosphorescent Polymer Light-Emitting Diodes Enabled by a New Electron Transport Material,” Earmme, T.; Ahmed, E.; Jenekhe, S. A. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 4744-4748. Highlighted in Hot Topics Organic Electronics, Wiley.
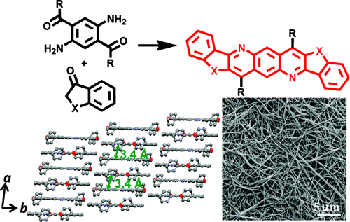
6. “Novel n-Type Conjugated Ladder Heteroarenes: Synthesis, Self-Assembly of Nanowires, Electron Transport and Electroluminescence of Bisindenoanthrazolines,” Ahmed, E.; Earmme, T.; Ren, G.; Jenekhe, S. A. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 5786-5796.
5. “Highly Efficient Phosphorescent Light-Emitting Diodes by Using an Electron-Transport Material with High Electron Affinity,” Earmme, T.; Ahmed, E.; Jenekhe, S. A. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 18448-18450.
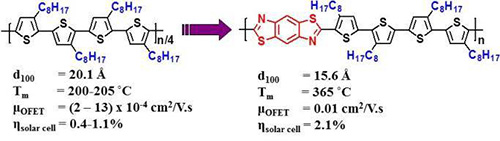
4. “Benzobisthiazole-Thiophene Copolymer Semiconductors: Synthesis, Enhanced Stability, Field-Effect Transistors, and Efficient Solar Cells,” Ahmed, E.; Kim, F. S.; Xin, H.; Jenekhe, S. A. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 8615-8618.
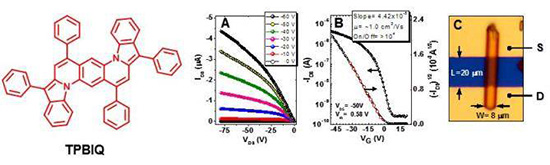
3. “High Mobility Single-Crystal Field-Effect Transistors from Bisindoloquinoline Semiconductors,” Ahmed, E.; Briseno, A. L.; Xia, Y.; Jenekhe, S. A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 1118-119. Highlighted in Synfacts.
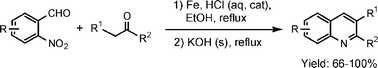
2. “A Highly Effective One-Pot Synthesis of Quinolines from o-Nitroarylcarbaldehydes,” Li, A-H.; Ahmed, E.; Chen X.; Cox, M.; Crew, P. A.; Dong, H-Q.; Jin, M.; Ma, L.; Panicker, B.; Siu, W. K.; Steinig, G. A.; Stolz, M. K.; Tavares, A. R. P.; Volk, B.; Weng, Q.; Werner, D.; and Mulvihill, J. M. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2007, 5, 61-64.
1. “New Finding on Interactions among the Yeast Oligosaccharyl Transferase Subunits Using a Chemical Cross-linker,” Yan, A.; Ahmed, E.; Yan, Q.; and Lennarz, W. L. J. Bio. Chem. 2003, 278, 33078-33087.